RFID on Metal: RFID Tags and Metal Surfaces
Originally Posted 4/10/13, Updated on 5/20/24

When it comes to RFID tags, mounting on or embedding in metal can be tricky, due to the metal interfering with the tag signal. RFID tag manufacturers have patented technology that allows RFID tags to work when attached to metal surfaces and even embedded within metal products.
As long as you choose the correct RFID equipment for your environment and application, you won't need to worry about interference from metal. Here are a few FAQ’s and tips to help you get started.
Contents
The Relationship Between Metal & RFID | Questions 1-3
Learn about Metal-Mount RFID Tags | Questions 4-6
Mounting on Metal | Questions 7-9
Metal-Mount RFID Tag Use Case Questions | Questions 10 & 11
Dealing with Metal in the RFID System Environment | Questions 12 & 13
1. Does metal interfere with RFID technology?
Metal surfaces reflect energy emitted from RFID readers and create interference for RFID tag antennas. The wave reflection that occurs when RF waves hit metal objects is just one reaction out of a few that can occur because RF waves are emitted in a variety of directions, called Multipath.
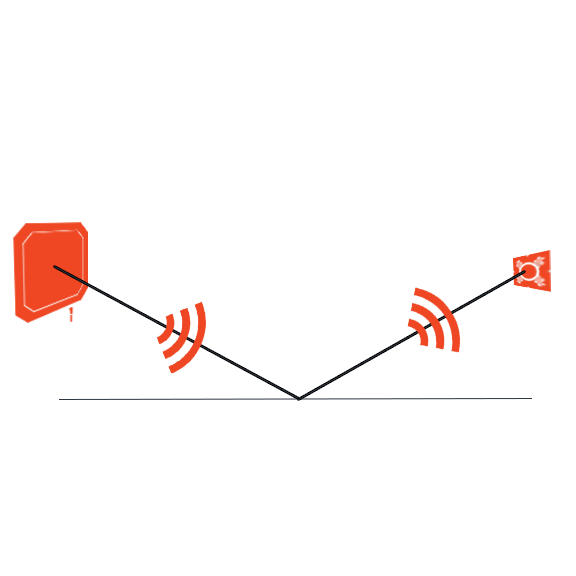
RF waves that reflect off of metal objects can potentially collide with other RF waves creating either destructive interference (null zones) or constructive interference.
Additionally, metal can “detune” RFID tags when the antenna inlay sits right against a metal surface. More information on this below.
Read more about multipath and RFID metal interference types here.
• • •
2. Is there a difference between tagging a metal object and metal in an environment?
Yes – tagging a metal object and metal objects in the application environment are very different.

Tagging a metal object
When an RFID tag is affixed to a metal object, the radio frequency (RF) waves bounce off the metal, directly back to the tag's antenna, rendering it ineffective. To address this issue, RFID tag manufacturers developed metal-mount tags specifically designed to mitigate the presence of metal and reflected RF waves.
Tagging a metal object will require an on-metal RFID tag that is specially designed to lift the tag’s antenna off the metal object with a small spacer. Furthermore, the tag possesses distinct characteristics that enhance its performance on metal surfaces, such as subtle adjustments in antenna tuning.

Metal objects in the environment
While addressing metal-related challenges in your RFID setup, it's important to note that not all metal elements will adversely affect your application. Generally, small metal objects are unlikely to cause issues, whereas larger items such as machinery, carts, or vehicles may potentially influence the read range and read zone of your system.
• • •
3. Why is it hard to tag metal objects?
Like mentioned above, metal reflects RF waves, and when that reflection occurs in the extremely small space between the RFID tag antenna and the metal object it is adhered to – the tag’s antenna detunes. If an RFID tag’s antenna detunes, it is no longer usable and must be replaced.
• • •
4. Which RFID tags work on metal assets?
Specialty RFID tags called metal mount RFID tags, or on metal RFID tags work well on metal surfaces. These tags are designed specifically for metal surfaces in the way that they are built – with a small spacer between the antenna and the object, and a specially tuned tag antenna designed to overcome any metal wave reflections.
Because of the addition of a spacer, most metal mount RFID tags are slightly bulkier than a typical label or RFID wet inlay.
There are also tags specifically designed to be embedded into metals, such as those intended for use in tool tracking applications. These tags are typically smaller, and made of a hard plastic or metal.
• • •
5. Are there different types of metal-mount RFID tags?
Yes – there are a few different types of metal-mount RFID tags in terms of attachment method and form factor.

Hard plastic metal mount tags
Most metal-mount tags are hard plastic RFID tags that having varying IP ratings for rugged or harsh environments. They can be attached onto metal assets with rivets, screws, epoxy, embedded, zip ties, or even extra strength adhesives.
RFID metal mount labels
Metal-mount RFID labels are similar to inlays, but with a thick foam layer for RF wave absorption. These labels can be run through specialized RFID printers for printing and encoding features and then adhered to a metal asset or item.
RFID flagtags
Flagtags are unique in that they do not use foam spacers, but instead use their unique size and shape to pull the RFID tag antenna off of the metal object. They are called ‘flagtags’ because the adhesive is located on one side and the RFID tag is on the other, lifted off the metal object, similar to a flag. Flagtags are mostly available in an inlay or label form factor, but there are also a few with a hard plastic, rugged shell.
• • •
6. How can you attach an RFID tag on a metal object?
The attachment method that works best for metal-mount RFID tags depends on the tag itself, its form factor, and the metal object that is being tracked. The most common ways to attach on metal RFID tags include:
- Screws
- Rivets
- Embedding
- Welding
- Adhesive (Extra-strength)
- Epoxy
- Zip Ties

Most hard plastic metal-mount tags, like the Confidex Ironside tag can be attached a few different ways depending on your preference. Welding the tag to a metal surface can ensure a more permanent hold, but it can also be affixed to surfaces with screws, pop rivets, and industrial adhesives.
Other tags like the Xerafy Dash can be embedded within metal objects before and after the point of manufacture, at which point they are sealed with epoxy to provide extra protection. This method of application along with the small size of the tag makes it popular in healthcare and other industries tracking small medical tools.
If you need printable RFID tags that work with metal, a few RFID tags are available that attach directly to metal surfaces with adhesive or foam adhesive. Several of these tags feature a paper face, so you can print logos, product information, or scannable 1d or 2d barcodes directly on the label.
• • •
7. Can RFID tags work inside of metal objects?
When an RFID tag is completely enclosed within a metal object, it cannot be read; however, if one side is not covered by metal, the RFID tag can be read with an RFID reader. Most companies simply use epoxy on one side and an embeddable, metal-mount RFID tag in a crevice or hole of a metal object.
To learn more about embeddable RFID tags – take a look at our infographic.
• • •
8. Can on-metal RFID tags withstand harsh conditions?

Because so many metal surfaces are exposed to harsh conditions, many RFID on-metal tags are specially designed and equipped to withstand harsh conditions. These rugged RFID tags are typically encased within a hard shell and will survive hard impacts, moisture exposure, and extreme temperatures.
• • •
9. Can on-metal RFID tags work on any metal surfaces?
Yes, on-metal RFID tags generally have no problem working on a variety of different types of metal assets including aluminum, steel, iron, copper, lead, and titanium. However, some tags designed specifically for on-metal applications will not perform as well on other surfaces such as glass, cardboard, or plastic.
• • •
10. Which industries are using metal mount tags?
RFID on metal tags are ideal for metal assets, metal inventory items, machinery and equipment, and tools. With the recent developments in RFID technology, metal mount RFID tags are becoming more popular in industries like automotive manufacturing, healthcare, industrial manufacturing, IT (information technology), aerospace and defense, oil and gas, and many others.
• • •
11. What types of objects are tagged with metal-mount RFID tags?

Below are a few of the most popular metal objects that are tagged with metal mount RFID tags:
- IT Assets – laptops, servers, radios
- Vehicles – production vehicles, finished vehicles
- Healthcare Assets – medical equipment, medical tools, carts
- Pipes and Pipe Spools
- Machinery & Equipment
- Tools – hammers, wrenches, mowers, power saws
- Oil Drums
- Kegs
- Car Parts and Components
- Returnable Containers, Carts
• • •
12. What type of metal objects in an environment could cause problems?
Most of the time, the larger the metal object in the environment, the more problematic the multipath effects. Metal objects that typical cause problems include large machinery, equipment, vehicles, and metal racking.
• • •
13. How can you mitigate problems caused by metal objects in the environment?
Most of the time, the RF waves will reflect off large metal objects in a variety of different angles which could cause the reflected RF waves to collide with the original RF waves, creating a null zone. The more metal in the environment, the more reflected RF waves.
To mitigate the problem, place RF absorbing materials like foam in front of the metal objects, change the angle of the RFID antenna, or place the RFID system closer to the RFID tag and lower the transmit power for a closer read zone.
Conclusion
If you would like help choosing a metal mount RFID tag, you can contact the sales engineers at atlasRFIDstore.com by emailing info@atlasRFIDstore.com or calling (205) 383-2244.
If you would like to learn more about all things RFID, check out our website, our YouTube channel, comment below, or contact us.
To read more about RFID tags, check out the links below!

